History is a vast ocean of knowledge, filled with the stories and legacies of countless civilizations. Among these, the history of Islam and Muslims holds a unique place, rich with profound impacts and contributions to the world. However, there is often confusion between the terms ‘Islamic history’ and ‘Muslim history,’ leading to a blurred understanding of these intertwined yet distinct concepts.
Islamic history and Muslim history are integral to our global heritage, shaping societies, cultures, and knowledge throughout the centuries. Yet, distinguishing between the two is crucial for appreciating their unique contributions and understanding their broader implications.
Many people use the terms “Islamic history” and “Muslim history” interchangeably, but they refer to different aspects of the past. Clarifying this distinction helps us appreciate the diversity and depth of the Muslim world.
This article explores the difference between Islamic and Muslim history, defines each term and its scope, and highlights their unique aspects.
Note:
- “Civilization” is the preferred spelling in American English.
- “Civilisation” is the preferred spelling in British English, Australian English, and other parts of the English-speaking world that follow British spelling conventions.
In the Islamic Hijri Calendar:
- BH: Represents “before Hijra,” the period before Prophet Muhammad’s migration (Hijra) from Mecca to Medina.
- AH: Represents “after Hijra,” the period after this migration (Hijra) from Mecca to Medina.
What is Islamic History?
Islamic history refers to the historical development of Islam as a religion, encompassing its theological, jurisprudential, and spiritual aspects.
The study of Islamic history delves into various aspects, such as theology, law, art, architecture, science, and philosophy. It explores how Muslim civilizations flourished through trade routes like the Silk Road and contributed significantly to advancements in mathematics, astronomy, and medicine through conquests and exchanges with other cultures, such as Byzantine and Persian societies.
Key Characteristics and Components
Islamic history delves into the essential doctrines of Islam, including the Quran, Hadith (the sayings and actions of Prophet Muhammad), and Sharia (Islamic law). It explores theological debates, religious practices, and the spread of Islamic teachings across different regions.
Historical Periods and Significant Events
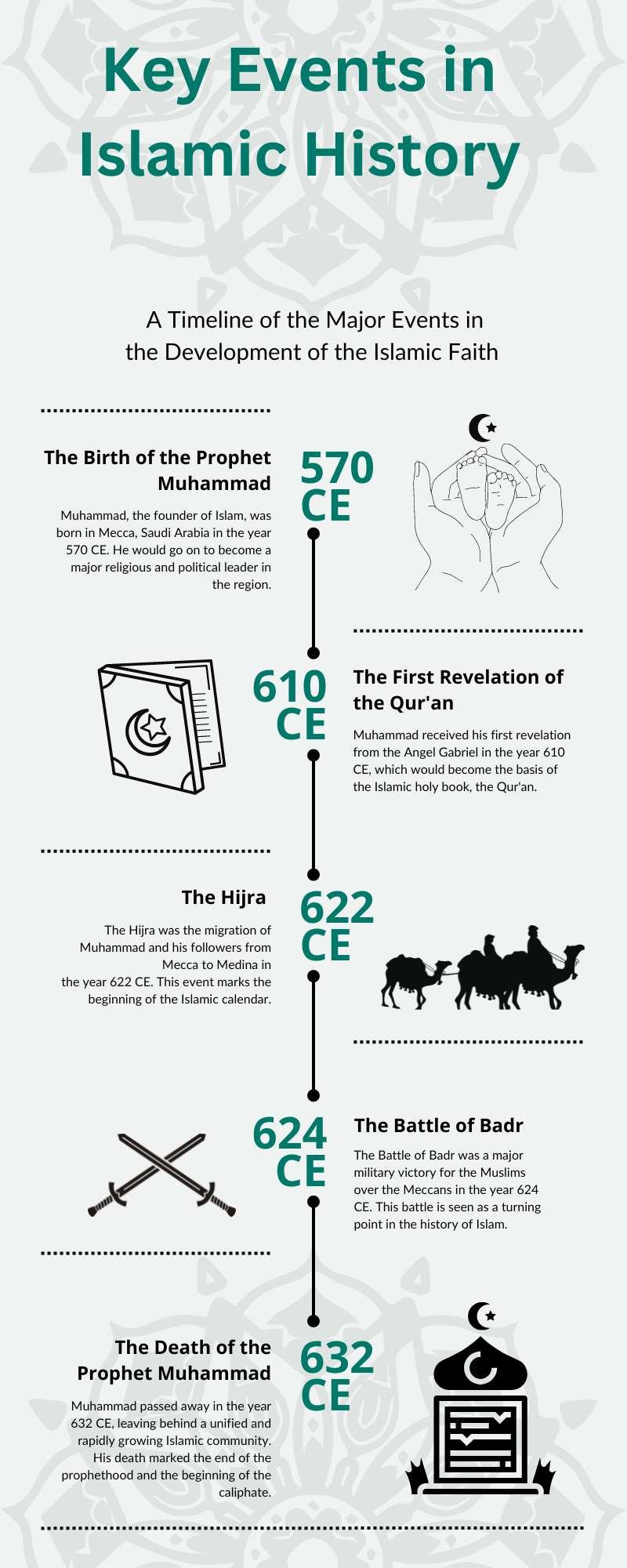
Islamic history covers pivotal events such as:
- The life of Prophet Muhammad (570-632 CE, 53 BH- 11 AH).
- The Revelation of the Quran (609-632 CE, 13 BH – 11 AH).
- The establishment of the first Islamic state under the constitution of Medina (622 CE, 1 AH).
- The Rashidun Caliphate (632-661 CE, 11-41 AH).
- The Umayyad (661-750 CE, 41-132 AH), Abbasid (750-1258 CE, 132-656 AH), and Ottoman Caliphates (1299-1922 CE, 699-1341 AH).
- The spread of Islam to various parts of the world.
Examples
- The Hijra (622 CE, 1 AH): The migration of Prophet Muhammad from Mecca to Medina, marking the beginning of the Islamic calendar.
- The Battle of Badr (624 CE, 2 AH): A decisive battle that solidified the early Muslim community’s strength.
Scope of Islamic History
Remember, history isn’t just about dates; it’s about stories, struggles, and shared humanity.
Islamic history spans a vast geographical area, from the Arabian Peninsula to Africa, Asia, and Europe. It includes the cultural and religious transformations within these regions influenced by Islamic teachings.
Influence on Global History
Islamic history has significantly impacted global history, spreading knowledge, science, art, and culture. Islamic civilization played a crucial role during the Golden Age of Islam (8th to 13th centuries), preserving and enhancing the knowledge of ancient civilizations.
Contributions to Various Fields
Seeing the fact that Prophet Muhammad (Peace be upon Him) places immense importance on seeking knowledge, highlighting how deeply embedded this value is in Islamic tradition.
- “Seek knowledge from the cradle to the grave.”
- “Seeking knowledge is an obligation upon every Muslim.” (Sunan Ibn Majah, Book 1, Hadith 224)
- “The ink of the scholar is more sacred than the blood of the martyr.” (Various narrations)
- “The superiority of the knowledgeable person over the worshiper is like that of the moon over all other heavenly bodies.” (Abu Dawood)
- “He who follows a path in quest of knowledge, Allah will make the path of Jannah (Paradise) easy for him.” (Sahih Muslim)
Islamic civilization has profoundly contributed to science, medicine, mathematics, astronomy, literature, and philosophy, laying the groundwork for many modern disciplines.
- Science and Medicine: Scholars like Ibn Sina (Avicenna) and Al-Razi (Rhazes) made groundbreaking contributions.
- Mathematics: Al-Khwarizmi’s work in algebra.
- Philosophy: Ibn Rushd (Averroes) and Al-Ghazali’s philosophical discourses.
The Islamic Golden Age significantly preserved and translated knowledge from ancient civilizations like Greece, Rome, and India. This knowledge was then transmitted to Europe, mainly through Muslim Spain (Andalusia), which served as a cultural and intellectual bridge between the Islamic world and medieval Europe.
What is Muslim History?
Muslim history refers to the historical experiences, achievements, and societal developments of Muslim communities worldwide.
Muslim history, on the other hand, focuses on the experiences and achievements of people who identify as Muslim. It encompasses political events, social movements, cultural expressions, and everyday life within Muslim communities worldwide.
It extends beyond theology to encompass the broader Muslim experience, their culture, art, science, and socio-political contributions.

Key Characteristics and Components
Muslim history includes the social, political, and cultural aspects of Muslim societies, encompassing diverse ethnicities, languages, and traditions.
Muslim history explores the rise and fall of empires, the emergence of artistic traditions like calligraphy and miniature painting, and the diverse social structures within Muslim societies. It examines the lives of prominent figures like caliphs, rulers, scientists, poets, and military leaders alongside the everyday lives of ordinary people.
Historical periods and significant events
Muslim history is rich with significant events, such as:
- The spread of Islam to Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia.
- The establishment and decline of Muslim empires (e.g., Umayyad, Abbasid, Ottoman).
- The Golden Age of Islam and its intellectual flourishing (800-1300 CE, 132-656 AH).
- Colonialism and the post-colonial period.
Examples
- The Abbasid Caliphate’s Golden Age (8th to 13th centuries, 132-656 AH) saw advancements in science, culture, and knowledge.
- The Mughal Empire’s architectural marvels, like the Taj Mahal.
- The Ottoman Empire: A significant political and cultural force from the 14th to early 20th centuries.
Scope of Muslim History
The scope of Muslim history extends beyond geographical boundaries, encompassing diverse regions like the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, Persia, Central Asia, South Asia, and Southeast Asia. It explores interactions with other civilizations through trade networks, diplomatic relations, and cultural exchanges.
Influence on Global History
Muslim history has profoundly influenced global history, from trade and exploration to exchanging ideas and cultural practices. Muslims were pivotal in connecting different parts of the world through trade routes like the Silk Road.
Contributions to Various Fields
- Art and Architecture: The development of distinctive Islamic architectural styles.
- Literature and Poetry: Contributions of poets like Rumi and Hafiz.
- Political Thought: The governance models and administrative innovations of Muslim empires.
Muslim history vs Islamic history
Understating the difference between Muslim history and Islamic history is essential for a nuanced understanding of the Muslim world, helping to appreciate its religious and cultural diversity.
- Islamic History: Focuses on the religious and theological evolution of Islam.
- Muslim History: Encompasses the socio-political and cultural experiences of Muslims.
- Islamic History: Centered on religious doctrines and the spread of Islamic teachings.
- Muslim History: Focuses on Muslim communities’ broader cultural, social, and political experiences.
- Islamic History: Involves religious texts, theological debates, and religious institutions.
- Muslim History: Encompasses daily life, governance, cultural expressions, and societal changes.
Example
- Islamic History: The development of Islamic jurisprudence (Fiqh) and the spread of Sufi orders.
- Muslim History: The rise and fall of the Ottoman Empire, the intellectual contributions of Muslim scholars in medieval Spain.
Let’s take a Case Study: Studying the Abbasid Caliphate through Islamic history reveals the development of Islamic Jurisprudence and legal institutions. However, Muslim history within the Abbasid period might highlight the experiences of different ethnicities, the rise of social classes, or the emergence of artistic movements like Arabic calligraphy.
This raises another question:
What is the History of Islam?
The history of Islam refers to the chronological account of the Islamic religion, from its birth to its current status as a global faith.
The history of Islam encompasses both Islamic and Muslim history, tracing the evolution of the religion itself from Prophet Muhammad’s revelations to the present day. It explores significant milestones like the codification of the Quran, the development of Islamic sects like Sunni and Shia, and the spread of Islam through trade, conquest, and missionary activities.
Key Characteristics and Components
The history of Islam encompasses the revelation of the Quran, the life of Prophet Muhammad, the spread of Islam, and the evolution of Islamic practices and institutions over time.
Evolution Over Centuries
Islam has evolved through various phases, including:
- Prophetic Era (610-632 CE, 13 BH – 11 AH)
- Rashidun Caliphate (632-661 CE, 11-41 AH)
- Umayyad Caliphate (661-750 CE, 41-132 AH)
- Abbasid Caliphate (750-1258 CE, 132-656 AH)
- Islamic Golden Age (8th-13th Centuries, 132-656 AH)
- Fragmentation and Regional Dynasties (10th-15th Centuries, 400-900 AH)
- Ottoman Empire (1299-1922 CE, 699-1341 AH)
- Colonialism and Imperialism (18th-20th centuries, 1100-1400 AH)
- Modern Era (Nationalism and Independence) (20th Century-Present, 1300 AH onwards)
Major Milestones and Timelines
- 610 CE, 13 BH: The first revelation to Prophet Muhammad.
- 622 CE, 1 AH: The Hijra to Medina.
- 632 CE, 11 AH: The death of Prophet Muhammad.
- 661-750 CE, 41-132 AH: The Umayyad Caliphate.
- 750-1258 CE, 132-656 AH: The Abbasid Caliphate.
- 15th-20th Centuries, 900-1400 AH: Ottoman Empire, colonialism, and the struggle for independence.
Key Figures and Events
This includes studying the lives of key figures like caliphs, imams, and reformers, alongside analyzing pivotal moments like the Crusades, the Mongol invasions, and the rise of modern Islamic movements.
- Prophet Muhammad: The founder of Islam.
- Caliphs Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali: The Rashidun Caliphs who succeeded Prophet Muhammad.
- Al-Ghazali, Ibn Sina, Ibn Khaldun: Scholars who made lasting contributions to philosophy, medicine, and historiography.
Scope of the History of Islam
The history of Islam covers the religious, political, and cultural dimensions of Islam, reflecting its growth and influence over centuries. It includes the development of Islamic institutions, the spread of Islamic civilization, and the ongoing challenges and transformations in the modern era.
Conclusion
Muslim history and Islamic history, though interconnected, focus on different aspects of the past. Islamic history revolves around Islam’s religious and theological development. In contrast, Muslim history encompasses Muslim communities’ broader socio-political and cultural experiences.
Understanding both histories is crucial for a comprehensive Muslim worldview, appreciating its religious foundations and diverse cultural expressions.
Recognizing the difference between Muslim history and Islamic history helps us appreciate the complexity and richness of the Muslim heritage. It fosters a deeper understanding of the Muslim world, promoting intercultural dialogue and mutual respect in our increasingly interconnected global society.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Islamic History?
Islamic history refers to the historical development of Islam as a religion, including its theological, jurisprudential, and spiritual aspects. It encompasses significant events, religious practices, and the spread of Islamic teachings.
2. What is Muslim history?
Muslim history refers to the historical experiences, achievements, and societal developments of Muslim communities worldwide. It covers political events, social movements, cultural expressions, and everyday life within these communities.
3. What is the history of Islam?
The history of Islam refers to the chronological account of the Islamic religion, from its birth to its current status as a global faith. It includes significant milestones such as the revelations to Prophet Muhammad, the development of Islamic sects, and the spread of Islam through trade, conquest, and missionary activities.
4. What is the Difference Between Islamic and Muslim History?
Islamic history focuses on the religious development of Islam, while Muslim history encompasses the social, political, and cultural experiences of Muslim communities.
5. What is the distinctions between Muslim history vs Islamic history?
Islamic History: Focuses on the religious and theological evolution of Islam.
Muslim History: Encompasses the socio-political and cultural experiences of Muslims.
Islamic History: Centered on religious doctrines and the spread of Islamic teachings.
Muslim History: Focuses on Muslim communities’ broader cultural, social, and political experiences.
Islamic History: Involves religious texts, theological debates, and religious institutions.
Muslim History: Encompasses daily life, governance, cultural expressions, and societal changes.
6. What are the key periods in the history of Islam?
Prophetic Era (610-632 CE, 13 BH – 11 AH)
Rashidun Caliphate (632-661 CE, 11-41 AH)
Umayyad Caliphate (661-750 CE, 41-132 AH)
Abbasid Caliphate (750-1258 CE, 132-656 AH)
Islamic Golden Age (8th-13th Centuries, 132-656 AH)
Fragmentation and Regional Dynasties (10th-15th Centuries, 400-900 AH)
Ottoman Empire (1299-1922 CE, 699-1341 AH)
Colonialism and Imperialism (18th-20th centuries, 1100-1400 AH)
Modern Era (Nationalism and Independence) (20th Century-Present, 1300 AH onwards)
7. What are some significant events in Muslim history?
Significant events in Muslim history include the spread of Islam to Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia, the establishment and decline of Muslim empires like the Umayyad, Abbasid, and Ottoman, the intellectual flourishing during the Golden Age of Islam, and the experiences of Muslim communities during colonial and post-colonial periods.
8. What was the Golden Age of Islam?
The Golden Age of Islam (800-1300 CE, 132-656 AH) significantly preserved and translated knowledge from ancient civilizations like Greece, Rome, and India. This knowledge was then transmitted to Europe, mainly through Muslim Spain (Andalusia), which served as a cultural and intellectual bridge between the Islamic world and medieval Europe.
References
- Armstrong, Karen. Islam: A Short History. Modern Library, 2002.
- Esposito, John L. The Oxford History of Islam. Oxford University Press, 1999.
- Lapidus, Ira M. A History of Islamic Societies. Cambridge University Press, 2014.
- Ahmed, Akbar S. Islam Today: A Short Introduction to the Muslim World. I.B. Tauris, 2001.
- Marshall G. S. Hodgson, The Venture of Islam: Conscience and History in a World Civilization, University of Chicago Press, 1974.

5 thoughts on “Difference between Islamic and Muslim History: A Comprehensive Guide”